http://www.wysap.com/xuexi/sales/20130421/1650.html
I'll come back later for detail!
2013年7月20日星期六
2013年7月16日星期二
Digest-Billing Plan-2

Check this out!
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_dimp50/helpdata/EN/dd/56163b545a11d1a7020000e829fd11/content.htm
Almost the same with the Digest-Billing Plan-1,but it contains more info..
 Customizing
Customizing 
UseThe following Customizing settings have to be made for down payment processing:Settings for the billing plan:To activate the billing plan function, maintain the materials, for which you wish to process down payments, with item category group 0005 (milestone billing). This gives the item type TAO via item type determination. The item type TAO calls up the billing plan function.
You need to implement the following activities in the billing plan for down payments:
- Maintaining the deadline type: This determines the billing rule (percentage or value down payment) for the down payment request.
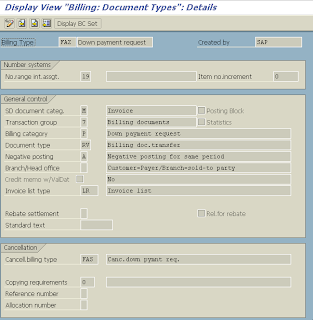
- The system assigns billing type FAZ (payment request) defined in the standard system with billing category P. (For the billing type FAZ there is the cancellation billing document type FAS in the standard system).
- Maintaining deadline proposal: Use the down payments that are due for the proposed deadlines.
- In the standard system the condition type AZWR is delivered for the down payment value already provided but which has not yet been calculated. You must include this condition type in the relevant pricing procedure before output tax.
- Enter condition 2 (item with pricing) and the calculation formula 48 (down payment clearing value must not be bigger than the item value) for the condition type AZWR.
- Before the condition AZWR you can create a subtotal with the base value calculation formula 2 (net value). If the condition AZWR is changed manually, you can get information on the original system proposal from the subtotal.
- Maintain the printing indicator.
- The pricing procedure can not be marked as a transaction-specific pricing procedure (field Spec.proc.)
- The condition type AZWR has the calculation type B (fixed amount) and the condition category E (down payment request / clearing).

No statistical or inactive conditions are set in a down payment item. If you require these conditions, use the user exit USEREXIT_PRICING_COPY in include RV61AFZA.
- In the standard system there is the billing type FAZ (down payment request) and for cancelling the billing type FAS.
- Controlling the down payment is done using the billing category P of the billing type. A billing type becomes a down payment request when the billing category P is assigned.
- You have to maintain blocking reason 02 (complete confirmation missing) for the billing documents and assign it to billing type FAZ.
- Copying control:
Copying requirement 23 must be entered in copying control at item level for down payment clearing. In the standard system the order type TA for copying control is set up according to the billing type F2 for the item category TAO.
- Set reconciliation accounts (transaction OBXR)
- Maintain accounting configuration (transaction OBXB)
You must also carry out a G/L account number assignment for the tax account.
- Maintain the posting key (transaction OB41)
- Maintain the field status definition (transaction OB14)
- Assign the company code to the field status variants (transaction OBC5)

2013年7月9日星期二
浮夸歌词
浮夸歌词
有人问我,我就会讲
但是无人来。
我期待,到无奈有话要讲,得不到装载
我的心情犹像樽盖等被揭开,咀巴却在养青苔
人潮内,愈文静愈变得不受理睬,自己要搞出意外
像突然,地高歌,任何地方也像开四面台
着最闪的衫,扮十分感慨
有人来拍照要记住插袋
我期待,到无奈有话要讲,得不到装载
我的心情犹像樽盖等被揭开,咀巴却在养青苔
人潮内,愈文静愈变得不受理睬,自己要搞出意外
像突然,地高歌,任何地方也像开四面台
着最闪的衫,扮十分感慨
有人来拍照要记住插袋
你当我是浮夸吧
夸张只因我很怕,似木头
似石头的话,得到注意吗
其实怕被忘记,至放大来演吧
很不安,怎去优雅
世上还赞颂沉默吗,不够爆炸~
怎麽有话题,让我夸做大娱乐家
那年十八,母校舞会
站着如喽罗
那时候我含泪发誓各位
必须看到我。
在世间,平凡又普通的路太多
屋村你住哪一座
情爱中,工作中,受过的忽视太多
自尊已饱经跌堕
重视能治肚饿
末曾获得过便知我为何
大动作很多犯下这些错
搏人们看看我算病态麽
你当我是浮夸吧
夸张只因我很怕,似木头
似石头的话,得到注意吗
其实怕被忘记,至放大来演吧
很不安,怎去优雅
世上还赞颂沉默吗,不够爆炸~
怎麽有话题,让我夸做大娱乐家
夸张只因我很怕,似木头
似石头的话,得到注意吗
其实怕被忘记,至放大来演吧
很不安,怎去优雅
世上还赞颂沉默吗,不够爆炸~
怎麽有话题,让我夸做大娱乐家
幸运儿并不多
若然未当过就知我为何
用十倍苦心做突出一个
正常人够我富议论性麽
你叫我做浮夸吧
加几声嘘声也不怕
我在场
有闷场的话表演你看吗
够歇斯底里吗?
以眼泪淋花吧
一心只想你惊讶
我旧时似未存在吗?
加重注码
青筋也现形,
话我知
现在存在吗?
凝视我,
别再只看天花,我非你杯茶
也可尽情地喝吧
别遗忘有人在为你声沙
SAP实施Roll out项目经验谈(二)
SAP实施Roll out项目经验谈(二) (2008-12-23 15:19:33)
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_3eeba4010100c5vr.html
上一篇谈到roll out项目的实施主体思路及项目管理方面要注意的事项,本篇着重谈技术与数据方面的问题。
技术方面,由于上篇所讲到的诸多限制,与全新的项目也有所不同。本人只在后勤方面有所了解,因此只能简单谈一下后勤方面配置的注意事项。总的来说,就是要注意在做系统配置的时候,不要忽视了已经存在的东西。有些配置或许在原始项目中已经做了,而且不是使用的标准设置,在做roll out项目的时候就要特别引起注意,不要因为roll out把母公司的业务给搅乱了。
技术方面的问题不能分门别类地谈,比较零乱,只能说一点是一点了。
1. 语言问题。
尤其是在跨国roll out项目中,一定要注意语言的问题。比如,在国家设置中,如果选定了语言,则在发往别国的采购单上,国家代码是以本国语言显示的。如果实际业务中不能做成这样,国家代码里就不要去选这个语言,让系统根据登录的语言自动确定即可。
再如,采购单的form,是有多种语言的。如果要拷贝出来更改的话,一定要注意拷贝多种语言。只在一种语言下拷贝,有可能导致其他语言下的采购单出问题。
2. 数据分类
着重谈一下物料类型。在roll out项目中,很多都会涉及到公司间交易。不论是跨公司销售,还是公司间采购,如果这种公司间交易是采用系统标准的模式来做,都会涉及到同一个物料编码在多个工厂之间应用的问题。这时,一个物料是什么物料类型就成为一个很重要的问题。
物料类型里有获取类型的限制。比如ROH的物料一般是只允许外部采购,不允许自制的。而在公司间交易时,往往在这个工厂是原材料的东西,在另一个工厂应该是成品。这时候,如果把它设置为原材料物料类型,在另一个工厂就无法做生产了。
物料类型里也有视图控制。HAWA里是没有工作计划的视图的。如果某个工厂向另一工厂采购物料后直接销售,往往会把它设置为HAWA类型。但是在另一个工厂,它就是自制品,需要生产的。
诸如此类的问题往往会导致物料类型分类方面的麻烦,需要特别加以注意。
3. 采购批准策略
如果原始项目中没有使用批准策略,而在roll out的时候,子公司需要使用的话,要注意特性设置上用公司代码或者采购组织等区分开来,而不能简单地使用一个单据类型实现这个功能。
4. 物料特殊获取类型
在MRP2视图里有一个字段叫作special procurement type。这里可以定义物料在另一工厂生产。象这种涉及到公司间交易的字段要着重加以确认。
5. 输出条件记录
要记得用MN*去维护各种输出的条件记录。尤其在跨国公司中,要注意维护出口税条件类型。
6. 在基础数据的设置中注意国家的正确维护
比如shipping piont的国家设置,有时候直接从原始项目中的某个拷过来了,改的时候只注意地址细节之类,没有注意到国家是不同的。这个是很容易忽略的。因为国家这个概念太大了,一般不会去理会它。在跨国公司roll out时尤其要注意。
7. EDI配置
在roll out项目中,有时会用到公司间交易。公司间交易的发票自动入账可以通过EDI实现,所以要注意EDI的相关配置。
8. 税码设置
SAP有个专门的notes来说这个事情。跨公司销售时,在F2类型的发票上,税码是如何确定的呢?可以由出货工厂和客户所在国家来确定,也可以由销售组织和客户所在国家来确定。默认是前一种。如果要用后一种,要手工把notes打上。
9. ERS的使用
在原始项目中,一般只有外部供应商,不会启用ERS功能。但在roll out项目中,有可能会使用ERS,因为内部供应商一般来说是可信任的。
10. GR-Based IV
原始项目中一般都要启用基于收货的发票校验。但在公司间交易中,有可能会使用基于PO的发票校验。尤其是在使用公司间采购流程同时使用EDI传送发票时,最好使用基于PO的发票校验。这样在发货方发货做Billing之后,对方可以立即入账。如果启用基于收货的发票校验,则因为还没有做收货,会出现无法过账的IDOC。
11. MRP的运行范围
多个工厂联合运行MRP,在roll out项目中可能是经常遇到的。要注意修改相关的配置。
12. Client层级的字段选择
比如物料主数据,供应商主数据,inforecord等,都有client层级的或者事务代码层级的字段选择设置。在改动这一类设置的时候,一定要小心。本人曾经改动过一个物料主数据的设置,为了针对某个工厂设置某个字段,把原始项目的相关字段组全部改为工厂级,还原为原来的设置,只把需要的工厂下的该字段属性做了改动。最后却发现考虑不周,影响了其他已经上线的公司,造成了很不好的影响。
技术方面和数据方面,需要注意的地方很多。本文只是列出一些本人所了解到的一小部分而已,希望能够起到抛砖引玉的作用。
SAP实施Roll out项目经验谈(一)
SAP实施Roll out项目经验谈(一) (2008-12-23 10:11:30)
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_3eeba4010100c1ci.html
本系列文章主要讨论在SAP实施Roll out项目中需要注意的事项,包括思路与项目管理,技术细节与数据两个部分。
本文讨论项目实施实施的思路与项目管理方面。
Roll out项目,本身在很多方面不同于全新的实施项目。它在很多方面受制于Global的实施思路和系统配置的影响。这种影响主要体现在以下几个方面。
第一,业务流程限制
与全新项目不同,Roll out项目的业务流程都是已经定好了的。实施的过程是一个把已有的业务流程复制到另一个子公司的过程。这就从根本上规定,业务流程实现方式必须以母公司为模板。尤其是跨公司交易的业务,公司间采购,跨公司销售等,更是必须遵从母公司的流程。
第二,数据分类限制
全新的项目可以根据公司的需要去定制统计分析模板,关键数据,特征字段等,都可以自行设计;但在Roll out项目中,不可避免地要受到母公司统计分析要求的制约。比如物料类型定义,涉及统计分析的字段内容定义如客户组,物料组等。CO模块更是有很多定义好的结构,是必须要严格遵从不能更改的。
第三,实施过程限制
全新的项目可以按照ASAP的方法论进行项目实施。但在Roll out项目里则不一定。根据签订合同内容的不同,实施的过程有可能会不同于全新项目。比如某个项目的Roll out合同规定,该Roll out项目必须完全拷贝母公司的流程,不允许有子公司个性化设置。在这种前提下,业务流程调研这一步的工作就几乎被忽略了,实施重点只是业务实现和培训。实施团队的任务不是根据子公司的实际业务制定流程,而是主要负责把母公司的流程介绍给子公司,子公司严格按既定的业务流程操作。
第四,法律法规限制
这一点在跨国公司roll out项目中尤其明显。各个国家法律法规不尽相同,从而导致公司业务流程不完全相同,这是显而易见的。比如税种不同,海关规定不同,甚至业务操作模式不同。这些都要在Roll out项目中予以充分的考虑。
第五,实施时间限制
一般来说,Roll out项目的实施时间都会比全新项目的实施时间短。常规的Roll out实施一般是三到四个月,而全新项目一般至少要六个月以上。
由于诸多类似限制的存在,我们在做Roll out项目时,要从项目实施思路的层次确立指导思想,在项目管理的层次严格落实。指导思想的正确是项目成功的前提。不要认为这是空话套话,象天朝官员讲话一样。事实上,指导思想绝对是项目实施中至关重要的一个环节。平时注意不到它,是因为它不大会出错。一旦指导思想出了偏差,项目离失败就不远了。这一点适用于全新的项目和Roll out项目。
第一,在母子公司之间确定主次。
各个企业结构不同,母公司对子公司的控制力度也不同。有些公司母公司控制力非常强,大权独揽,相对于子公司来说,是我叫你干啥你干啥,没叫你干的你就别干;另一些公司,相对松散,子公司相对拥有较大的自由度,除了关键问题,子公司具有“我说了算”的权力。在做Roll out项目的时候,确定公司间的这种主次关系是首要的任务。就本次实施任务来说,是子公司说了算,还是母公司说了算?这一点要在参与实施的各方之间达成共识。
在项目组织的架构上,如果以母公司为主,则项目经理应该是母公司的派出人员;在实施过程中,项目经理对子公司与项目相关的部分应该有相对较大的决定权。子公司项目参与人员更多的是被动的接受,而不是在某些需要做决定的有争议的部分,指手划脚。如果以子公司为主,则项目经理应该是子公司的人员,或者母公司派出人员。项目实施过程中更多地考虑子公司自身的业务,母公司已经设置好的流程等只是作为参照。
曾经有一个项目,母子公司之间在这一点上没有达成共识。母公司认为子公司应该以复制母公司现有流程为主,基本不考虑额外的需求。如果有困难要从流程改变上去解决;但母公司又没有派出项目经理,甚至没有人全程参与,仅仅依靠实施顾问方进行知识转移,阻力之大可想而知。子公司参与人员没有理性的期望值,对项目要求过高。这种项目注定是不成功的。可能不是失败的,但最终效果一定是不理想的。
第二,注重与母公司的沟通。
对于roll out项目来讲,不仅仅要在项目内部进行沟通管理,而且要在项目与母公司之间进行顺畅的沟通管理。项目组必须要建立项目与母公司顺畅的沟通渠道。实施过程中,不可避免地会需要与母公司进行各方面的沟通。特别是有CR提出来时,如果迟迟得不到解决,会大大地拖延项目进行,也会严重影响到项目人员的积极性。
值得一提的是,不论是母公司为主,还是子公司为主,母公司一定要有熟悉项目的人参与到子公司的实施过程中来。一个熟悉原始项目的参与者带来的效益,好过一堆文档。相信大家对这一点是认同的。囿于时间,资金等限制,几乎没有什么项目能够在文档上做到与项目实际进程齐头并进,保证文档是最新最准确的。除非是一个专门以交付文档为目的的项目。在这个前提下,原始项目参与者带来的知识就显得异常重要。而且,很多东西是无法写在文档中的,它只存在于人的大脑里。没有原始项目人员的参与,roll out项目实施过程中,就只能不断地通过电话邮件等方式与母公司联系。这对项目进行的效率影响是相当大的。尤其是跨国公司,加上时差原因,沟通效果就更大打折扣。
第三,适当降低期望值。
无论是在全新实施项目中,还是在roll out项目中,这一点都是相当重要的。如果客户对项目的期望值过高,实施起来就会难度重重。优秀的咨询顾问,应该知道如何帮助客户建立适当的期望值。迫于签单的压力,销售人员往往会有意无意地夸大系统的功能,给后来的实施埋下隐患。顾问进场后,很重要的一个任务就是要管理客户的期望值。
尤其是在roll out项目中,要先给客户定下调子,这个项目不可能有很多的自由度,或许有很多实际的业务流程无法在系统中满足,只能通过更改现有的操作习惯的方式来解决实际问题。在数据分类,跨公司业务等涉及到全球模板的方面,要想更改是很不容易的,除非有特别的理由。
当客户对系统能够实现的功能有了较为合理的定位时,项目推进过程中就会避免很多抱怨。客户的主要精力才会由压迫顾问做事,转向自我改良去适应全球模板要求。
这并不是敷衍客户。全球模板之所以能被推广,一般来说不会有什么根本性的缺陷。某个子公司的特殊需求,经过认真分析,大部分可以在全球模板中找到解决的方案。
第四,给予培训工作更多的重视。
对于全新的项目来讲,事前的流程讨论,业务蓝图的设置,需要用去很多的时间。这部分的工作做得越仔细,越认真,后续的系统实现和测试等就会越顺利。而在这整个过程中,关键用户都是全程参与的,无形之中他们已经学习了很多系统知识。同时,由于项目时间久,关键用户对系统的了解是由浅入深逐步进行的,会有时间去消化所学到的内容,后来的操作培训就会相对容易一些。
但对于roll out项目来讲,流程讨论部分其实是全球模板的介绍,仅对不符合实际业务的部分进行讨论和定义。由于时间短,关键用户没有太多的时间去理解系统的逻辑,对他们不可避免地要实行填鸭式培训,效果也相对差一些。常常是学了前面忘了后面。另一方面,由于系统功能已经经过原始项目的完整测试,一般来说在测试过程中出现的问题也少一些,关键用户通过测试发现问题,了解问题出现的原因的过程中,学到的知识也会相对较少。由此,培训工作在roll out项目中就要占据更大的比重。
第五,整理数据时注意全局性。
一般来说,roll out项目整理数据时,母公司的系统已经运行了一段时间。在数据的分类上,数据标准上,都已经有了现成的标准。更有许多物料供应商客户等数据,是母公司系统中已经存在的。因此在数据搜集和整理的过程中,要特别注意这一点。要过滤母公司已经存在的数据,新的数据定义,分类要与母公司保持一致。
从项目管理角度来说,要想避免冗余数据或者错误定义,应当由母公司对数据进行检查。但往往这是一个不可能的任务。因此,顾问应该对数据搜集投入一定的精力。这里又有一个矛盾。一般来说,数据搜集是客户的任务,顾问只提供模板,不参与实际的搜集整理过程。我认为,这是一个很不好的现象。数据是SAP系统运行的基础,如果数据做不好,系统的运行就不会令人满意。顾问作为系统专家,应该参与到数据搜集当中去。最好是在项目合同中就明确,顾问应该参与数据搜集整理,当然,咨询公司因此要得到一定的报酬。还要界定责任,顾问应当主动检查用户数据,并提出专业的意见。事实上,客户在搜集数据的过程中,也经常会向顾问请教。但是主动的参与和被动的指导,其效果肯定是大不一样的。这一点,不论是全新项目还是roll out项目都适用。
第六,上线切换注意关联交易。
上线时的切换工作方面,roll out项目和全新项目有一些不同。主要体现在跨公司业务方面。在子公司上线时,母公司往往已经运行了一段时间,且与子公司有业务往来。未清的跨公司交易业务如何处理?这是在roll out项目中要考虑的。在全新的项目中则不必考虑这一点,只需考虑到对客户,对供应商的未清业务即可。而公司间交易与外部客户和供应商显然有不同之处。
总之,roll out项目不同于全新项目,在项目管理的指导思想上,项目经理要区别对待,针对性地加强对相关环节的控制。
2013年7月1日星期一
Digest-Billing Plan-down payment condition type (azwr)
LO615 Billing中的一个练习。感觉这是一个相对不错的练习(培训中大部分练习感觉都是鸡肋) 一个down payment的billing过程涉及到了billing
plan以及FI clear过程。短短几步但是可以看出billing plan的作用和clear的过程。
-1 Create a standard order (OR) for customer
T-S66F## (sales organization 1000,
distribution channel 10
and division 00). This customer orders an elevator (material
number: T-FS2##). The
purchase order number is ##LO615-AZ.
2-1-1 Go to the billing
plan.
Select the item and choose →→
goto->item->billing plan
2-1-2 Create an invoice
for the down payment request.
Enter the order number above and choose the to
restrict the dates as described above.
=> Billing type FAZ is used for billing the down payment request
2-1-3 The customer paid
the down payment that was figured into the invoice. Post the payment.
Accounting->FI->Customer->Document
Entry->Down Payment->Down payment
Doc Date: current date
customer account: 1280
Special G/L indicator: A
Bank Account:113100
Amount: Refer FI Doc generated by billing doc
Choose Request
Select the down payment requests in the list and choose .
Save.
2-1-4 Now execute the
milestone billing process for the first settlement period
=> Two items appear in the billing document:
The amount from the first partial billing document and the down payments made by the customer that still need to be settled
2-1-5 How could you
arrange for the down payment to be only partially calculated, into the first partial invoice?
Condition type AZWR is used especially for down payment processing. If you only want to carry out partial settlement, you can select the down payment item to be settled in the billing document, branch to the pricing screen, and change the value of condition type AZWR.
2-1-6 Check the document
flow for this order.
IDES与培训环境数据对应:
Company
code
1000
1000
Sales organization
1000
1000
Distribution channel 10 or
14
10 or 14
Division
00
00
Shipping
point
1200
1200
Plant
1200
1200
Customer
T-S66A##
2141
T-S66B##
2141
T-S66C##
2141
T-S66D##
2141
T-S66E##
1171
T-S66F##
1280
Materials
T-ASA##
M-06
T-ASB##
M-07
T-ASC##
M-08
T-ASD##
M-09
T-ZS2##
REPAIR_SERVICE
T-FS2##
E-1002
配置见HELP
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_dimp50/helpdata/EN/dd/56163b545a11d1a7020000e829fd11/content.htm
配置见HELP
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_dimp50/helpdata/EN/dd/56163b545a11d1a7020000e829fd11/content.htm
BILLING PLAN中相关的配置,关键是 REFENCE 参考 0000000435
然后就可以在VF01中按F1类型开 形式发票了;
定价条件还需要考虑 SO中的 PAYMENT TERMS,注意AZWR被用到了~
http://scn.sap.com/thread/1501610
http://scn.sap.com/thread/759515
有关AZWR的2个帖子。
SO FAR~
Digest-Billing Plan-1
Start
From
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_46c/helpdata/en/dd/560674545a11d1a7020000e829fd11/content.htm
From
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_46c/helpdata/en/dd/560674545a11d1a7020000e829fd11/content.htm
Billing Plan
Purpose
A billing plan is a schedule of individual billing dates for a single item in a sales document. You can define a billing plan at header level, which is then valid for all items assigned to it.
Depending on the kind of business process you are carrying out, the system can automatically propose one of two different types of billing plan: periodic billing or milestone billing.
- Periodic billing means billing a total amount for each individual billing date in the plan. For example, if you are creating a rental contract, the system can propose a schedule of monthly rental payments, according to the length and conditions of the contract.
- Milestone billing means distributing the total amount to be billed over multiple billing dates in the billing plan. For example, you can use a billing plan for billing a make-to-order item that is assigned to a project in the SAP Project System. When you enter the project-related make-to-order item in the sales order (or assembly order), the system proposes a billing plan based on milestones defined for networks in the project. As each milestone is successfully reached, the customer is billed either a percentage of the entire project cost or simply a pre-defined amount.
During sales order processing, the system determines from the item category whether a billing plan is required and, if so, which type of plan: The type of billing plan that is determined at this point is set up in Customizing and cannot be changed in the sales document. For each billing plan you create, you can enter a freely-definable search term in the details screen of the billing plan in the sales document. When you save the document, the system automatically assigns a number that later uniquely identifies the individual plan. You can use the search term later to locate specific billing plans.
Billing plans for rental contracts and billing plans for project-related milestone billing have different overview screens so that you can enter data relevant to your processing. For example, for milestone billing, you must be able to enter data to identify the individual milestones.
简单来说,物料主数据-销售视图-(工厂,销售组织,分销渠道)
所以在标准(OR)的SO 中ITEM项,ITEM CATEGORY=TAO
见配置
AND
所以会有带出BILLING PLAN中的MILESTONE BILLING!!!
SAP SD从零开始-转自http://space.itpub.net/11037-(05-07)
5 从库存销售
销售凭证类型Sales document type:
用来鉴别和控制不同的业务流程类型;
标准的销售凭证类型:
standard order;
Rush order;
cash sales;
free-of-charge delivery;
returns;
Contract;
Consignment fill-up;
Credit/Debit request;
销售凭证功能Sales Document Functions
通过销售凭证类型直接或间接地active或deactive;
功能:
Delivery scheduling;
Transfer of requirements;
Pricing;
Sales Info System;
Credit check;
Output;
Text;
Availability Check;
交货起运点Shipping Point
Shipping Point是R3中负责交货(shipping)的组织单元;
可以在Shipping Point中定义准备和装卸货物的时间;
Shipping Point通常为销售凭证中的每个行项目所确定;
路线Route:
起点/终点,可分为几段;
可以用Route来为运输计划定义实际的运输时间和前置时间;
自动确定shipping Point:
根据3个key来搜索:
交货条件shipping condition:Sold-to-party 客户主记录中定义;
装卸组loading group:物料主记录中定义;
出货工厂delivering plant:见出货工厂的自动确定(Lesson 4);
MARK:可以用交货条件来定义客户需求;
自动确定Route:
根据4个key来搜索:
出发地区departure zone:shipping point中定义;
交货条件shipping condition:Sold-to-party 客户主记录中定义;
运输组transportation group:物料主记录中定义;
目标地区transportation zone:ship-to party客户主记录中定义;
交货计划Delivering Scheduling
订单发行日期Order date;
物料可用日期Material availability date;
运输计划时间Transport planning;
装载日期Loading date;
发货日期Goods issue date;
交货日期Delivery date:到达客户;
运输计划Transportation Scheduling
运输时间 transit time;
运输前置时间Transportation lead time;
回溯计划Backward scheduling
交货和运输计划的目的是确定客户物料的交期;
物料筹备日期和运输计划日期可根据客户要求的交货日期计算出来;外向交货单outbound delivery必须在此两个日期最早的那个创建;
前向计划Forward scheduling
当回溯计划的结果显示客户要求的交期无法达成时,使用前向计划;
物料最早可用的时间是新的物料筹备日期;outbound delivery日期是新的物料筹备日期和运输计划日期中早的那一个;
对销售凭证的ITEM,会有2条计划行项目产生:
第一条计划行的日期对应客户要求的交货日期,没有确认数量;
第二条计划行显示的是确认的交货期和确认金额;
集中交货处理Collective Processing in shipping
在系统中建立Outbound delivery依赖于shipping point、selection date 和 其他条件;
一旦你设置了这些标准,就能够控制选择到期应该shipping的业务;选择的可选项因Delivery的场景和用户的角色不同而变化;
当设置了选择日期(selection date),就定义了当日到期item会被考虑集中delivery处理;此日期是货物能够按时到达客户的最晚开始Shipping处理的时间;它对应物料筹备日期或者运输计划日期;
Outbound Delivery选项
完全交货Complete Delivery;
部分交货Partly Delivery;
合并交货 Order Confirmation;
不同订单合并的条件:
相同的shipping point;
Delivery到期的日期相同;
相同的ship-to-party;
相同的route;
相同的Inco terms;
出货流程中的检配Picking in Shipping Process
Picking是从创建Transfer request开始的;Transfer request中的行项目包括物料及数量,对应Outbound Delivery中的delivery的数量;
集中Picking处理Collective processing in Picking
系统自动地将outbound delivey的项目合并到尽可能少的transfer request中;
Picking选项Picking Options
从transfer request打印picking list/传送到外部WMS系统;
手动/自动确认;
如果全部数量无法满足:
产生另外一个新的tansfer request;
将Picked 的数量copy到Outbound delivery的delivery数量;(部分交货)
集中出货处理Collective processing for Posting Goods Issue
系统自动地将outbound delivey的项目合并到尽可能少的document中;
集中开票处理Collective Processing in Billing
系统提供billing due list来实现一次处理多张billing document;
系统自动地将项目合并到尽可能少的billing document中;项目可以是order中的也可以是outbound delivery中的(系统中配置)
合并的条件:
same billing date, the same ship-to party, payer or terms of payment;
Billing选项Billing Options
发票分割Invoice split:
eg: 1张outbound delivery对应1张sales order,
2张billing document对应1张outbound delivery;
每张交货单单独开票Separate billing document for each outbound delivery:
eg: 2张outbound delivery对应1张sales order,
2张billing document对应2张outbound delivery;
集中开票Collective invoice:
eg: 3张outbound delivery对应2张sales order,
1张billing document对应3张outbound delivery;
Worklist在SD中的集中处理:
Delivery list:处理order到outbound delivery;
Picking worklist:处理outbound delivery到transfer request;
Goods issue worklist:处理outbound delivery到goods issue;(Picking完成)
Billing Due list:处理outbound delivery(/order)到billing;(Goods issue完成)
6 销售凭证类型
销售中的业务流程控制Controlling Business Processes in sales
销售流程通过销售凭证(sales documents)的配置来控制;
销售凭证的配置可在凭证头Header、行项目Item、计划行schedule line层次,依赖于凭证的结构,
对应的控制工具为销售凭证类型Sales Document type、行项目类型Item Category、计划行类型Line Schedule Category;
需要配置以实现Item Category和Schedule Line Category在销售凭证中自动带出;
在Copy Control中可以根据你的需要配置数据从销售凭证传送到后续凭证的内容;
基本功能Basic Functions
必须为销售凭证定义一些基本功能,否则销售凭证就没有配置完成;
这些基本功能包括:
Partner determination;
Pricing;
Output determination;
Text determination;
Material determination;
Credit management;
Incompletion checks;
Delivery scheduling etc.
可以为不同的Sales Document Type使用不同的功能;
销售凭证类型的功能Functions in sales document type
号码分配Number assignment;
缺省值Default Value:
Date,billing type,delivery type,blocks;
检查Check:
Division,Open Quotations/contracts,Info Record;
MARK:Check会影响性能;
合同增强Enhancement for contracts;
分配基本功能Assigning basic
强制参考Mandatory reference
MARK:增加一个销售凭证类型到销售流程中是非常耗时的,因为在配置中很多输入都是依赖于销售凭证类型的;所以最好是Copy现有的;
修改销售凭证类型Changing The Sales Document Type
当修改销售凭证上的销售凭证类型时,必须确保:
没有后续的凭证;
不是状态相关的后续凭证;
凭证不是从service notification 或者contract创建;
行项目类别可以修改;
MARK:如果试图修改已经保存的凭证的凭证类型,2个凭证类型必须属于相同的号码范围;
销售区域允许的订单类型Order Types permitted for sales areas;
可以定义销售凭证的有效范围:
销售组织Sales organizations
分销渠道Distribution channels
产品组Divisions
7 行项目类别
Item Category的例子:
系统交付的不同的Item category支持不同的业务流程,可以根据它来创建自定义的;
定义为4位的key;前2位提示销售凭证类型,后2位显示Item category的作用;
AFTX Sales document type: IN Usage: TEXT;
TAD Sales document type: OR Item category group: LEIS;
KMN Sales document type: NMS Item category group: NORM;
Item Category的作用:
控制Item在销售凭证及后续的业务处理流程中的行为;
Item Category的本质特怔决定:
行项目的业务数据是否允许不同于头部;
价格是否应用于Item;
Item是否和如何做Bill;
Item是否引用另外一个item,或它是否仅仅是一个文本行;
哪一个incompletion log用来Check the item data;
可以修改标准系统中定义的Item category的设置,也可以通过COPY/Change来定义新的Item category;
Delivery相关标记delivery relevance indicator 是仅适合没有计划行的Item,例如可以Text Item中MARK它,则系统会将该ITEM从sales order copy到Delivery document;
作用:
区分业务数据separate business data;
计划行允许Schedule Lines permitted;
交货相关delivery relevance;
开票相关Billing relevance;
定价Pricing;
物料清单BOMs;
完成规则completion rule;
分配基本功能Assigning basic functions;
控制销售凭证中的行项目:
销售凭证中的每个行项目是通过Item category来控制的;这样可以:
在不同的销售凭证中使用不同的Item category;
在销售凭证中为每个Item实现不同的业务处理流程;
标准订单中Item category的判定:
销售凭证中的Item category是通过销售凭证类型sales document type和物料主记录中的行项目类别组item category group来查找的;
子项目Sub-items:
可以将行项目分配给更高层的行项目,例如客户订购一定数量的的商品(10)将获得免费赠送的商品(20);在20的higher-level item field中输入10;
其他应用sub-item的例子包括BOMs展开和Service 项目;
MARK:除了sub-item,可供选择的项目Alternative items 也可以记录在报价和询中,但是它的处理不同于sub-item,例如Alternative items不包含在凭证的净值中;
BOMs的例子:
所有你想要在销售凭证中控制的BOM items都必须标记为‘relevant for sales’;
当BOM使用类型BOM usage 5创建的BOM中的所有项目会自动标记为销售相关;
在销售凭证的Item category中作了适当的设置之后,你只需要输入BOM的料号就可以将BOM中的所有组件COPY到销售订单中;
BOM以主-子main and sub-items 的形式出现在销售凭证中,系统自动展开BOM为组件生成子项目;
在销售凭证中展开BOM:
在销售凭证中,有许多独立的Item Categorys控制BOM的行为,配置时,你为销售凭证中的BOM的main和sub-item定义和分配item category;
在main item的物料主记录中定义的item category group定义了哪种item category分配给了main item;
为了判定销售凭证中BOM要展开到什么程度,需要为main item定义item category结构的广度extent;
当你判定了sub-item,系统也需要知道上层item的item category;
在item category的配置中,你可以控制哪些item与定价有关以及怎样实现需求传递requirements transfer;
订阅:
博文 (Atom)